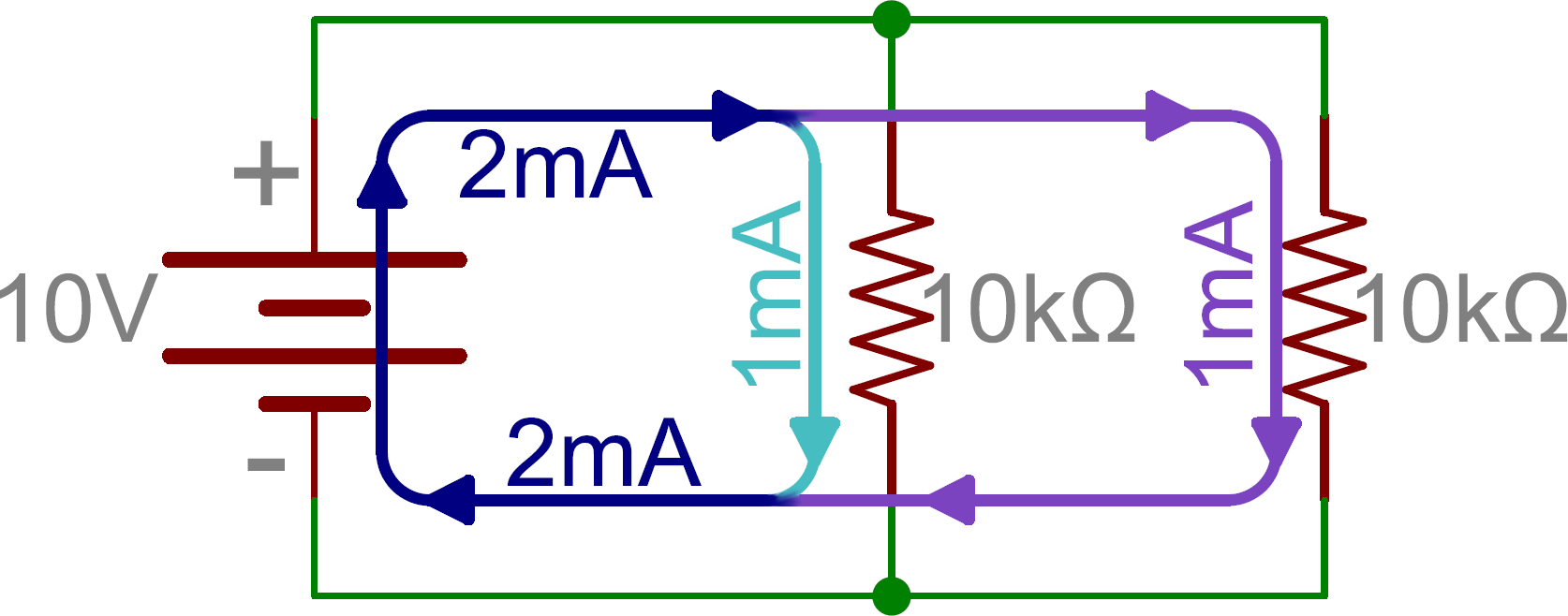
Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel . Figure 21.4 shows resistors in parallel, wired to a voltage source. resistors connected in parallel have the same voltage drop, but the currents flowing through. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. Resistors are in parallel when each resistor. resistors in parallel have the same numerical voltage drop because they are connected. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. resistors in parallel. in this introduction to parallel resistance circuits, we will explain the three key principles you should know: In this chapter, we introduced the equivalent. If two or more resistors are connected in parallel, then the potential difference across each resistor is same.
from learn.sparkfun.com
Resistors are in parallel when each resistor. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. in this introduction to parallel resistance circuits, we will explain the three key principles you should know: the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. resistors in parallel have the same numerical voltage drop because they are connected. If two or more resistors are connected in parallel, then the potential difference across each resistor is same. Figure 21.4 shows resistors in parallel, wired to a voltage source. resistors in parallel. resistors connected in parallel have the same voltage drop, but the currents flowing through. In this chapter, we introduced the equivalent.
Series and Parallel Circuits
Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel Resistors are in parallel when each resistor. Figure 21.4 shows resistors in parallel, wired to a voltage source. If two or more resistors are connected in parallel, then the potential difference across each resistor is same. in this introduction to parallel resistance circuits, we will explain the three key principles you should know: Resistors are in parallel when each resistor. resistors in parallel have the same numerical voltage drop because they are connected. resistors connected in parallel have the same voltage drop, but the currents flowing through. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. In this chapter, we introduced the equivalent. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. resistors in parallel.
From open.ocolearnok.org
Resistors in Series and Parallel Physical Science Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel If two or more resistors are connected in parallel, then the potential difference across each resistor is same. In this chapter, we introduced the equivalent. Resistors are in parallel when each resistor. resistors in parallel. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. the. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From rccrestauracao.blogspot.com
Series Parallel Resistor Calculator Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel If two or more resistors are connected in parallel, then the potential difference across each resistor is same. resistors in parallel. resistors in parallel have the same numerical voltage drop because they are connected. In this chapter, we introduced the equivalent. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From electricalacademia.com
Parallel Circuit Definition Parallel Circuit Examples Electrical Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel Figure 21.4 shows resistors in parallel, wired to a voltage source. in this introduction to parallel resistance circuits, we will explain the three key principles you should know: If two or more resistors are connected in parallel, then the potential difference across each resistor is same. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From www.khadley.com
Resistors in series and parallel Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. resistors connected in parallel have the same voltage drop, but the currents flowing through. resistors in parallel have the same numerical voltage drop because they are connected. Figure 21.4 shows resistors in parallel, wired to a. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From fity.club
Resistors In Parallel Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel resistors connected in parallel have the same voltage drop, but the currents flowing through. resistors in parallel have the same numerical voltage drop because they are connected. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. resistors in parallel. the current entering a. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From www.youtube.com
Resistors in Electric Circuits (14 of 16) Calculating Voltage for Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel in this introduction to parallel resistance circuits, we will explain the three key principles you should know: the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From learn.sparkfun.com
Series and Parallel Circuits Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. in this introduction to parallel resistance circuits, we will explain the three key principles you should know: Resistors are in parallel when each resistor. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From www.youtube.com
Current Division Example Problem 1 (Parallel Resistors) YouTube Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel resistors connected in parallel have the same voltage drop, but the currents flowing through. resistors in parallel. In this chapter, we introduced the equivalent. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. Figure 21.4 shows resistors in parallel, wired to a voltage source. . Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From www.allaboutcircuits.com
Resistors in Parallel Understanding Current and Voltage in Parallel Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel If two or more resistors are connected in parallel, then the potential difference across each resistor is same. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. In this chapter, we introduced the equivalent. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From control.com
The Difference Between Series and Parallel Circuits Basic Direct Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel resistors in parallel have the same numerical voltage drop because they are connected. In this chapter, we introduced the equivalent. in this introduction to parallel resistance circuits, we will explain the three key principles you should know: Figure 21.4 shows resistors in parallel, wired to a voltage source. If two or more resistors are connected in parallel, then. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From circuitdiagramceria.z22.web.core.windows.net
How To Solve Combo Circuits Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel In this chapter, we introduced the equivalent. Figure 21.4 shows resistors in parallel, wired to a voltage source. resistors in parallel. If two or more resistors are connected in parallel, then the potential difference across each resistor is same. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From owlcation.com
Resistors in Series and Parallel Formula Derivation Owlcation Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. In this chapter, we introduced the equivalent. resistors in parallel. in this introduction to. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From www.youtube.com
Resistors in series and parallel YouTube Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel resistors connected in parallel have the same voltage drop, but the currents flowing through. resistors in parallel have the same numerical voltage drop because they are connected. In this chapter, we introduced the equivalent. If two or more resistors are connected in parallel, then the potential difference across each resistor is same. resistors in parallel. the. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From www.tpsearchtool.com
Electric Circuit Resistors In Parallel Definition And Diagram Images Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel Resistors are in parallel when each resistor. In this chapter, we introduced the equivalent. resistors in parallel have the same numerical voltage drop because they are connected. resistors connected in parallel have the same voltage drop, but the currents flowing through. Figure 21.4 shows resistors in parallel, wired to a voltage source. If two or more resistors are. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Two resistors R1 and R2 (where R1 > R2) are connected Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. If two or more resistors are connected in parallel, then the potential difference across each resistor is same. resistors in parallel. In this chapter, we introduced the equivalent. resistors connected in parallel have the same voltage. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From electricalacademia.com
Resistors in Series and Parallel Electrical Academia Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel in this introduction to parallel resistance circuits, we will explain the three key principles you should know: In this chapter, we introduced the equivalent. If two or more resistors are connected in parallel, then the potential difference across each resistor is same. Resistors are in parallel when each resistor. Figure 21.4 shows resistors in parallel, wired to a voltage. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From electricalacademia.com
Series Parallel Circuit Series Parallel Circuit Examples Electrical Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel resistors in parallel. If two or more resistors are connected in parallel, then the potential difference across each resistor is same. resistors connected in parallel have the same voltage drop, but the currents flowing through. In this chapter, we introduced the equivalent. Figure 21.4 shows resistors in parallel, wired to a voltage source. Resistors are in parallel when. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.
From paolaewataylor.blogspot.com
How to Calculate Total Resistance in a Series Parallel Circuit Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel In this chapter, we introduced the equivalent. resistors connected in parallel have the same voltage drop, but the currents flowing through. resistors in parallel have the same numerical voltage drop because they are connected. the current entering a parallel combination of resistors is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor in parallel. in. Current Voltage Resistors In Parallel.